 English
English שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Kurdî
Kurdî  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Malay
Malay  Türkçe
Türkçe  العربية
العربية  فارسی
فارسی  Burmese
Burmese  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski
How Does a High Pressure Rotary Jet Drilling Rig Create Soil-Cement Columns?
2025-12-02
How Does a High Pressure Rotary Jet Drilling Rig Create Soil-Cement Columns?
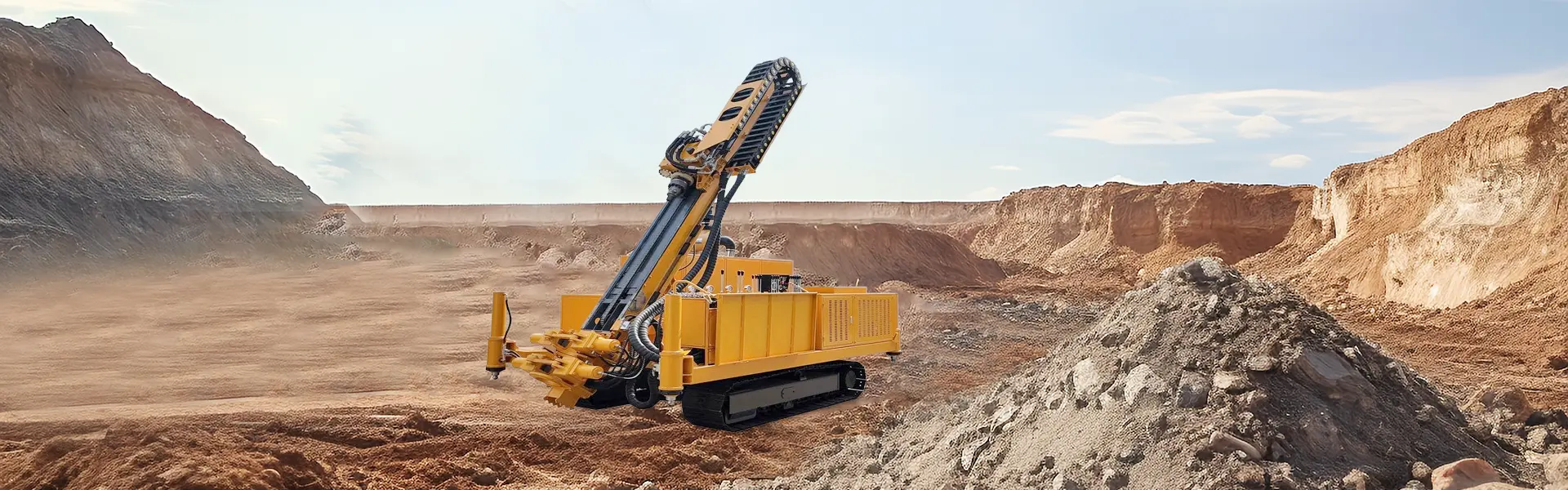
The creation of soil-cement columns using a high pressure rotary jet drilling rig is a sophisticated ground improvement technique that transforms weak, compressible soils into stable, load-bearing elements. Known internationally as jet grouting, this process involves the in-situ mixing of native soil with a cementitious grout slurry injected at extremely high pressures. The resulting soil-cement columns, or panels, can significantly increase bearing capacity, reduce settlement, and provide earth retention or hydraulic cut-off walls. The effectiveness of this method hinges on the immense energy delivered by the high-pressure fluid jet to erode and simultaneously mix the soil.
The process begins with the positioning of the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig at the designated column location. The rig then drills a guide hole to the required treatment depth using a relatively small-diameter drill string, often with the assistance of a lower-pressure fluid or air to remove cuttings and stabilize the borehole. This initial drilling phase ensures that the jet grouting string can reach the target zone without obstruction. Once the desired depth is achieved, the jet grouting operation commences. The drill string is connected to a high-pressure pump, capable of generating pressures typically ranging from 400 to 600 bar, and sometimes even higher. This pump forces a grout slurry through the drill rods and out through specially designed nozzles located at the base of the monitor, or jetting head.
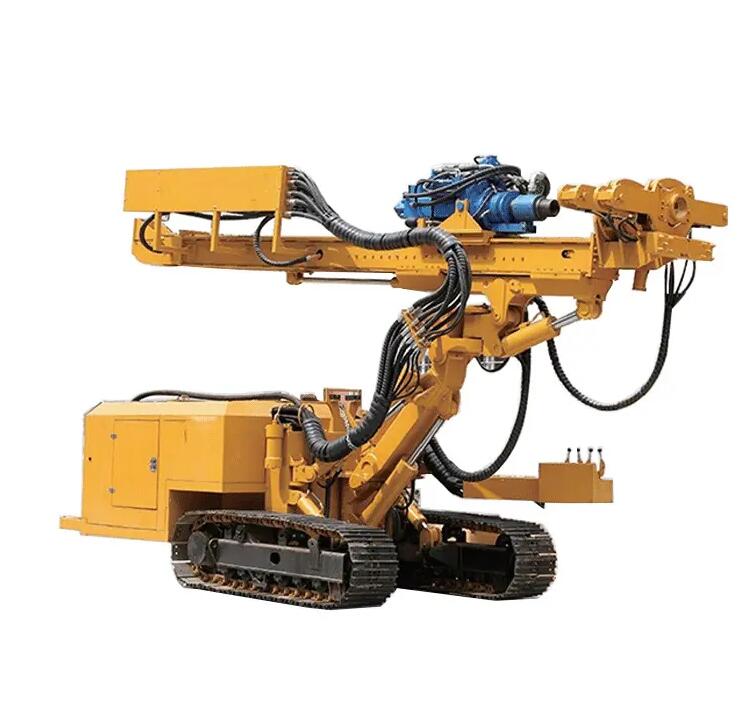

The core of the technology lies in the monitor and the jetting action. As the grout is expelled from the nozzles at supersonic velocities, it forms a coherent, high-energy jet that forcefully erodes the surrounding soil matrix. The high pressure rotary jet drilling rig then begins to rotate and slowly withdraw the drill string from the bottom of the hole upwards. The combination of rotation and withdrawal is carefully controlled to ensure a uniform column diameter. The erosive power of the jet creates a cavity that is simultaneously filled and mixed with the grout slurry. The parameters of withdrawal speed, rotation speed, and pump pressure are precisely calibrated based on the soil type and the desired column diameter; for example, slower withdrawal and higher pressure generally result in a larger diameter column.
There are several jet grouting systems, and the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig can be configured for the most common one, the Single Fluid System, described above. In this system, the grout slurry alone acts as the cutting and mixing medium. The soil particles are broken apart and blended with the cement grout to form a homogeneous soil-cement material. The properties of the final column, such as its strength and permeability, depend on the soil's original characteristics, the water-cement ratio of the grout, and the efficiency of the mixing. The process generates a significant amount of spoil—a mixture of excess grout and displaced soil—which returns to the surface along the annulus of the borehole. This spoil must be managed and collected in a containment system for later disposal or treatment.
The successful execution of this technique relies on rigorous quality control and an understanding of soil-jet interaction. Operators of the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig must continuously monitor and record all key parameters, including flow rate, pressure, rotation speed, and lift speed. Pre-production trials, or test columns, are often conducted to confirm the design assumptions and refine the operational parameters for the specific site conditions. These test columns are subsequently excavated or cored to verify their geometry and to test the strength of the recovered soil-cement samples. By controlling the energy input and the kinematics of the jet, the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig creates a predictable and competent soil-cement column that effectively reinforces the ground.




