 English
English שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Kurdî
Kurdî  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Malay
Malay  Türkçe
Türkçe  العربية
العربية  فارسی
فارسی  Burmese
Burmese  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski
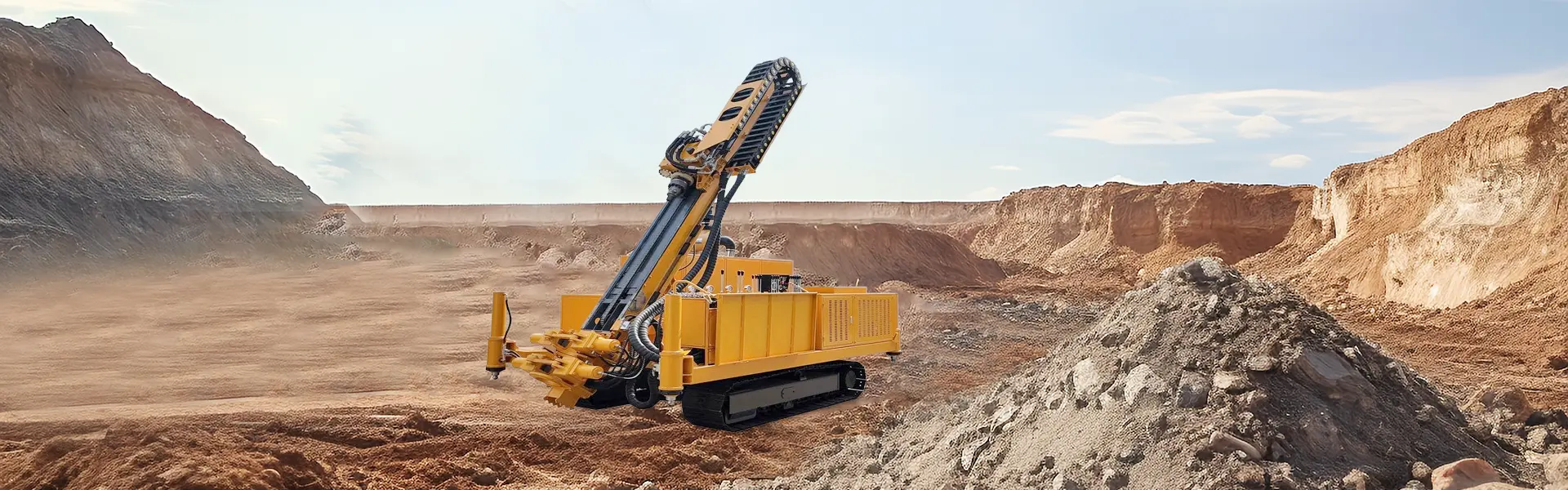
How Does a High Pressure Jet Rig Strengthen Weak Soil Foundations?
How Does a High Pressure Jet Rig Strengthen Weak Soil Foundations?
Weak, compressible, or liquefiable soil foundations pose significant challenges for construction, often leading to excessive settlement, bearing capacity failures, or seismic vulnerability. The high pressure rotary jet drilling rig offers a powerful solution to these problems through a ground improvement technique known as jet grouting. This method fundamentally alters the properties of the native soil by creating a composite material—soil-cement—that possesses significantly improved strength, stiffness, and impermeability. The process involves the injection of a cement grout slurry at extremely high pressures to disaggregate and mix with the in-situ soil.
The mechanism of strengthening begins with the immense kinetic energy of the fluid jet. Operated by a high pressure rotary jet drilling rig, the system pumps grout through small nozzles at the end of a monitor, generating a coherent, high-velocity jet that can exceed the speed of sound. This jet effectively erodes the soil structure, breaking the bonds between individual soil particles. In granular soils like sands and gravels, the jet forces the particles apart, creating a cavity. In cohesive soils like clays and silts, the jet shears and remolds the soil mass. This destructive phase is immediately followed by a constructive one, as the eroded soil particles are forcibly mixed with the cementitious grout slurry injected by the same jet.
The result of this in-situ mixing is the creation of a soil-cement column or panel. The geometry of this improved ground element can be controlled by the operation of the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig. By rotating and lifting the monitor at a controlled rate, a cylindrical column is formed. By lifting without rotating, a vertical panel or wall can be created. The properties of the final product are a function of the original soil type and the mix design. In sandy soils, the resulting material can achieve unconfined compressive strengths similar to soft rock, drastically increasing the foundation's bearing capacity. In clayey soils, the improvement often focuses more on reducing compressibility and creating a more homogeneous mass, thereby mitigating differential settlement.
The high pressure rotary jet drilling rig can be deployed to create various structural elements within the ground to address specific weaknesses. For increasing bearing capacity, a grid of overlapping jet grout columns can be constructed to form a continuous raft or pile-like elements that transfer structural loads to a more competent depth. This is a common solution for foundations of embankments, storage tanks, or building structures on soft ground. For stabilization of excavation sides and earth retention, the rig can create contiguous or secant pile walls that act as cantilevered retaining structures or be integrated with tie-back anchors. Furthermore, the very low permeability of the soil-cement mix allows the technique to be used for constructing hydraulic cut-off walls to control groundwater flow or to encapsulate contaminated soils.
The success of this foundation strengthening method is highly dependent on proper design and execution. The selection of operational parameters for the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig—including jet pressure, flow rate, rotation speed, and withdrawal rate—is tailored to the specific soil stratigraphy identified in the geotechnical investigation. Pre-construction test panels are often essential to verify the design diameter and strength of the columns. During production, rigorous monitoring and recording of all drilling and grouting parameters ensure consistency and quality. By transforming weak soil into a engineered composite material, the high pressure rotary jet drilling rig provides a versatile and effective means to create a stable and reliable foundation for a wide range of infrastructure projects.




