 English
English שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Kurdî
Kurdî  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Malay
Malay  Türkçe
Türkçe  العربية
العربية  فارسی
فارسی  Burmese
Burmese  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski
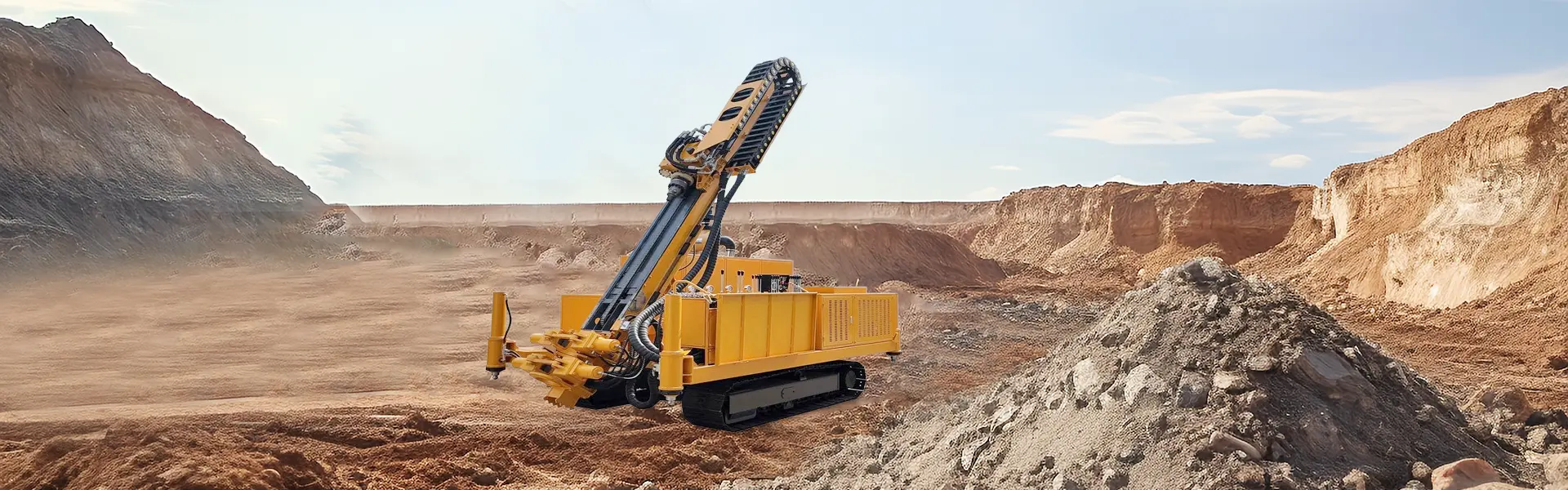
Detailed Explanation of Two Rock Breaking Methods for Multi Functional Anchoring Drilling Rig
2025-09-26
Detailed Explanation of Two Rock Breaking Methods for Multi Functional Anchoring Drilling Rig
The Multi Functional Anchoring Drilling Rig is one of the most common and critical equipment in engineering drilling operations. It employs only two rock breaking methods: one is rotary cutting, which is generally applied in rock formations with a hardness coefficient of f ≤ 8; the other is impact-rotary breaking, typically used in surrounding rock with a hardness coefficient of f ≥ 8.
Mechanism of Rotary Drilling Rig Rock Breaking
Rotary drilling rigs break rock by using multi-edge cutting bits to rotate and cut the rock, forming a circular borehole. Rotary cutting rock breaking requires the following conditions:
① The drilling rig must possess sufficient torque to overcome the resistance moment during bit cutting;
② The drilling rig must have a certain output speed to drive the rotation of the drill rod and bit;
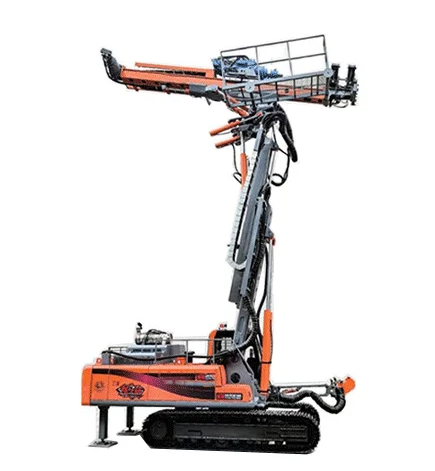

③ A certain axial thrust must be applied to the drilling rig, i.e., a specific positive pressure on the bit, to achieve the feed motion of the bit cutting.
Mechanism of Impact-Rotary Drilling Rig Rock Breaking
The rock breaking mechanism of impact-rotary drilling rigs is as follows: under the action of impact stress waves, the drill bit cuts the local rock surface beneath its edges at a certain impact frequency. While performing impact motion, the bit also rotates, enabling it to break the rock within a 360° range in the borehole. Impact-rotary rock breaking requires the following conditions:
① The rock drill must possess a certain impact energy and impact frequency;
② The output shaft of the rock drill must achieve 360° rotation while performing linear impact motion;
③ A certain axial thrust must be applied to the rock drill.
From the rock breaking mechanisms, it is evident that the Multi Functional Anchoring Drilling Rig uses rotary rock breaking primarily for drilling anchor holes in roadways with soft roof conditions, such as coal seams or semi-coal rock seams (generally with rock stability coefficient f < 8). In contrast, impact-rotary rock breaking is used for drilling in rock roadways with harder roof conditions (generally with rock stability coefficient f ≥ 8).




